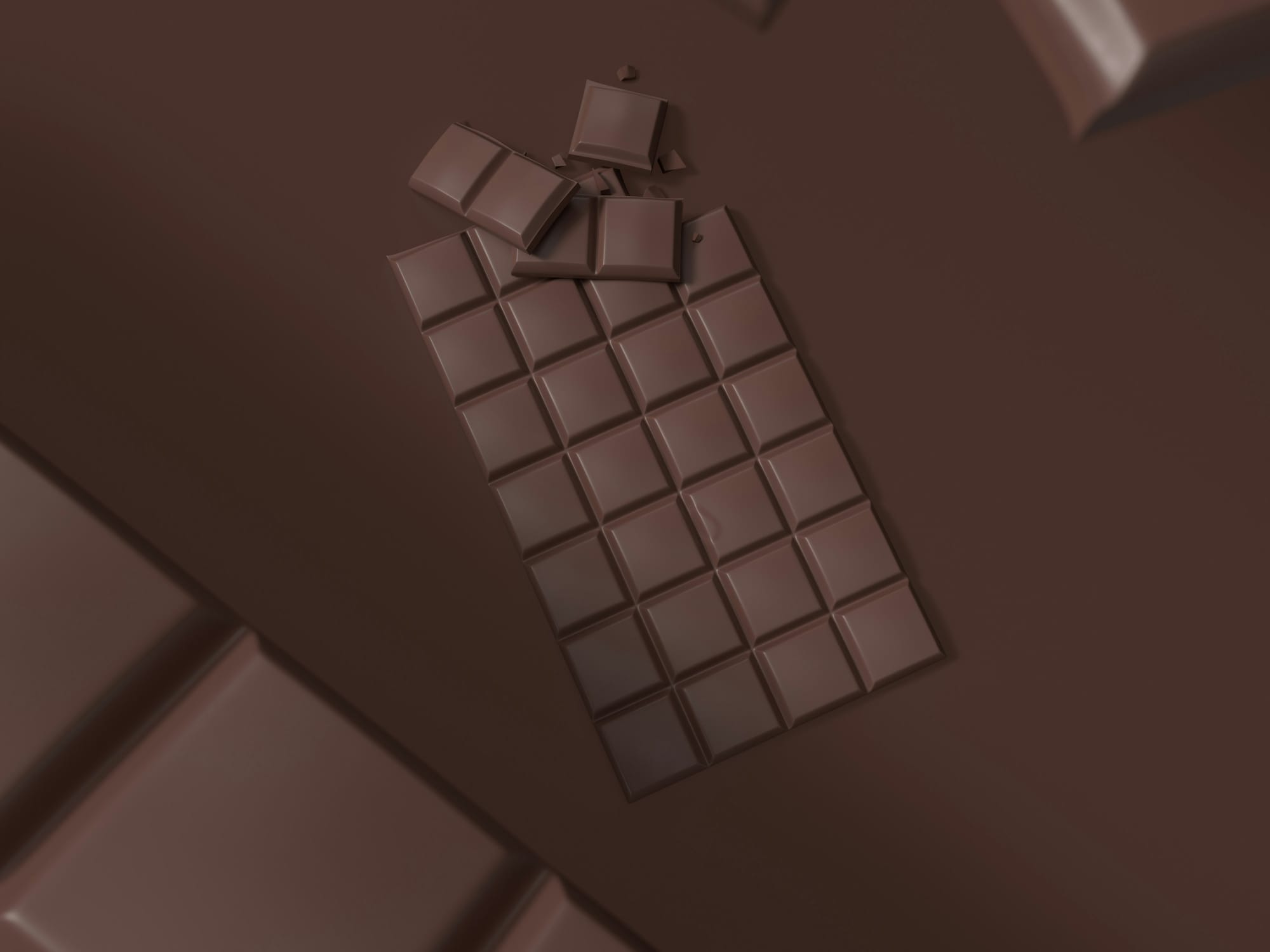
Imagine if your morning coffee or an evening square of dark chocolate could do more than satisfy cravings—what if they were actually helping your cells age more gracefully? Recent groundbreaking research published in December 2025 reveals that theobromine, a naturally occurring compound abundant in cocoa and present in coffee, may be linked to slower cellular aging. This discovery is reshaping how nutritionists and healthcare professionals view these beloved indulgences, transforming them from guilty pleasures into potential longevity allies.
The Science Behind Theobromine's Anti-Aging Promise
Theobromine is a bioactive alkaloid that comprises approximately 3.3% of cocoa beans by weight. While chemically similar to caffeine, it functions as a gentler central nervous system stimulant because it doesn't cross the blood-brain barrier as easily. A landmark study from King's College London analyzed blood samples from 1,669 participants across two European cohorts and found remarkable results: individuals with the highest theobromine levels showed slower epigenetic aging than those with the lowest levels.
The research team, led by Ramy Saad, utilized sophisticated biological markers, including GrimAge—an advanced epigenetic aging clock that predicts mortality risk, disease susceptibility, and lifespan-related biomarkers. According to Dr. Fady Hannah-Shmouni, an endocrinologist at the University of British Columbia who wasn't involved in the study, "GrimAge is one of the most advanced and researched epigenetic aging clocks" that can predict not just biological age but also the rate of aging itself. In the TwinsUK cohort, higher theobromine levels were associated with roughly 1.6 years of age acceleration per standard increase in theobromine concentration.
Understanding Biological Versus Chronological Age
The distinction between how many birthdays you've celebrated and how old your body actually is at the cellular level matters profoundly for health outcomes. Biological age reflects the physiological condition of your cells, tissues, and organs, influenced by lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and disease history. Scientists measure biological age through epigenetic changes—chemical modifications that turn genes "on" or "off" without altering the underlying DNA sequence.
The study also examined telomere length, another crucial aging biomarker. Telomeres are protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that shorten as we age, much like the plastic tips on shoelaces that prevent fraying. Participants with elevated theobromine levels demonstrated longer telomeres, though this relationship was weaker than the epigenetic aging markers, suggesting that theobromine may influence multiple, distinct aspects of the aging process.
Beyond Anti-Aging: Theobromine's Broader Health Benefits
The therapeutic potential of theobromine extends beyond cellular aging. Research published in 2024 indicates that theobromine improves lipid profiles and aids in weight management. An August 2025 study found that daily 450 mg theobromine supplements increased HDL2 cholesterol—the larger, more protective form of "good" cholesterol—by approximately 0.95 mg/dL over 12 weeks. Dr. Federica Amati, a registered public health nutritionist at Imperial College London, notes that "dark chocolate that's at least 70% cocoa and only contains a handful of ingredients can actually support good health" due to its rich concentration of bioactive compounds, including polyphenols, iron, magnesium, copper, and manganese.
Additionally, a large-scale study examining cognitive performance found that daily theobromine intake was positively associated with scores on delayed recall, animal fluency, and digit symbol substitution tests, suggesting potential neuroprotective benefits. The compound has also been linked to improved cardiovascular health markers, including reduced blood pressure and enhanced endothelial function.
Making Theobromine Work for Your Health
Not all chocolate is created equal when it comes to maximizing theobromine benefits. Highly processed chocolate products, laden with added sugars and emulsifiers, won't deliver the same health benefits. Choose dark chocolate with at least 70% cocoa content and minimal additional ingredients to ensure you're getting meaningful amounts of beneficial compounds. Coffee also contains theobromine, though in much lower concentrations than cocoa.
Lead researcher Ramy Saad emphasizes that "this is a very exciting finding," but cautions that important questions remain about the mechanisms behind these associations. Future randomized controlled trials with controlled theobromine doses will be essential to confirm these observational findings and establish optimal intake levels. While theobromine shows promise as an anti-aging compound, it should be viewed as one component of a comprehensive healthy lifestyle that includes balanced nutrition and regular physical activity.
The emerging science around theobromine represents a fascinating intersection of nutrition, epigenetics, and longevity research. As we continue to understand how dietary compounds influence aging at the molecular level, your daily chocolate habit may prove more beneficial than anyone previously imagined—provided you choose quality dark chocolate and maintain overall healthy habits.
Stay informed with reliable insights. Add Zilck.com as a preferred source in your Google settings to see our content prioritized in your search results. It's quick and easy—just visit your Google account preferences, navigate to "Preferred sources," and add Zilck.com to your list.
Get the information you trust, faster. Click the button below.












Discussion